From Bernard Cornwell's
Last Kingdom:
***
I do not know if King Edmund was a saint. He was a fool, that was for sure. He had given the Danes refuge before they attacked Eoferwic, and given them more than refuge. He had paid them coin, provided them with food, and supplied their army with horses, all on the two promises that they would leave East Anglia in the spring and that they would not harm a single churchman.
They kept their promises, but now, two years later and much stronger, the Danes were back, and King Edmund had decided to fight them. He had seen what had happened to Mercia and Northumbria, and must have known his own kingdom would suffer the same fate, and so he gathered his fyrd and prayed to his god and marched to do battle. First he faced us by the sea, then, hearing that Ivar was marching around the edge of the great watery wastes west of the Gewæsc, he turned about to confront him.
Ubba then led our fleet up the Gewæsc and we nosed into one of the rivers until the channel was so narrow our oars could not be used, and then men towed the boats, wading through waistdeep water until we could go no farther and there we left the ships under guard while the rest of us followed soggy paths through endless marshland until, at long last, we came to higher ground. No one knew where we were, only that if we went south we had to reach the road along which Edmund had marched to confront Ivar. Cut that road and we would trap him between our forces and Ivar’s army.
Which is precisely what happened. Ivar fought him, shield wall against shield wall, and we knew none of it until the first East Anglian fugitives came streaming eastward to find another shield wall waiting for them. They scattered rather than fight us, we advanced, and from the few prisoners we took we discovered that Ivar had beaten them easily. That was confirmed next day when the first horsemen from Ivar’s forces reached us.
King Edmund fled southward. East Anglia was a big country, he could easily have found refuge in a fortress, or else he could have gone to Wessex, but instead he put his faith in God and took shelter in a small monastery at Dic. The monastery was lost in the wetlands and perhaps he believed he would never be found there, or else, as I heard, one of the monks promised him that God would shroud the monastery in a perpetual fog in which the pagans would get lost, but the fog never came and the Danes arrived instead.
Ivar, Ubba, and their brother, Halfdan, rode to Dic, taking half their army, while the other half set about pacifying East Anglia, which meant raping, burning, and killing until the people submitted, which most did swiftly enough. East Anglia, in short, fell as easily as Mercia, and the only bad news for the Danes was that there had been unrest in Northumbria. Rumors spoke of some kind of revolt, Danes had been killed, and Ivar wanted that rising quenched, but he dared not leave East Anglia so soon after capturing it, so at Dic he made a proposal to King Edmund that would leave Edmund as king just as Burghred still ruled over Mercia.
The meeting was held in the monastery’s church, which was a surprisingly large hall made of timber and thatch, but with great leather panels hanging on the walls. The panels were painted with gaudy scenes. One of the pictures showed naked folk tumbling down to hell where a massive serpent with a fanged mouth swallowed them up.
“Corpseripper,” Ragnar said with a shudder.
“Corpseripper?”
“A serpent that waits in Niflheim,” he explained, touching his hammer amulet. Niflheim, I knew, was a kind of Norse hell, but unlike the Christian hell Niflheim was icy cold. “CorpseRipper feeds on the dead,” Ragnar went on, “but he also gnaws at the tree of life. He wants to kill the whole world and bring time to an end.” He touched his hammer again.
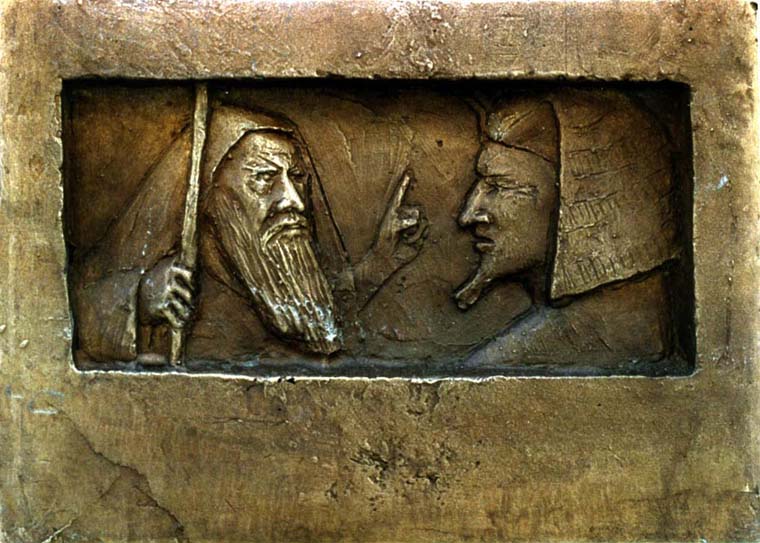
Another panel, behind the altar, showed Christ on the cross, and next to it was a third painted leather panel that fascinated Ivar. A man, naked but for a loincloth, had been tied to a stake and was being used as a target by archers. At least a score of arrows had punctured his white flesh, but he still had a saintly expression and a secret smile as though, despite his troubles, he was quite enjoying himself.
“Who is that?” Ivar wanted to know.
“The blessed Saint Sebastian.” King Edmund was seated in front of the altar, and his interpreter provided the answer. Ivar, skull eyes staring at the painting, wanted to know the whole story, and Edmund recounted how the blessed Saint Sebastian, a Roman soldier, had refused to renounce his faith and so the emperor had ordered him shot to death with arrows. “Yet he lived!” Edmund said eagerly.
“He lived because God protected him and God be praised for that mercy.”
“He lived?” Ivar asked suspiciously.
“So the emperor had him clubbed to death instead,” the interpreter finished the tale.
“So he didn’t live?”
“He went to heaven,” King Edmund said, “so he lived.”
Ubba intervened, wanting to have the concept of heaven explained to him, and Edmund eagerly sketched its delights, but Ubba spat in derision when he realized that the Christian heaven was Valhalla without any of the amusements. “And Christians want to go to heaven?” he asked in disbelief.
“Of course,” the interpreter said.
Ubba sneered. He and his two brothers were attended by as many Danish warriors as could cram themselves into the church, while King Edmund had an entourage of two priests and six monks who all listened as Ivar proposed his settlement. King Edmund could live, he could rule in East Anglia, but the chief fortresses were to be garrisoned by Danes, and Danes were to be granted whatever land they required, except for royal land. Edmund would be expected to provide horses for the Danish army, coin and food for the Danish warriors, and his fyrd, what was left of it, would march under Danish orders. Edmund had no sons, but his chief men, those who lived, had sons who would become hostages to ensure that the East Anglians kept the terms Ivar proposed.
“And if I say no?” Edmund asked.
Ivar was amused by that. “We take the land anyway.”
The king consulted his priests and monks. Edmund was a tall, spare man, bald as an egg though he was only about thirty years old. He had protruding eyes, a pursed mouth, and a perpetual frown. He was wearing a white tunic that made him look like a priest himself. “What of God’s church?” he finally asked Ivar.
“What of it?”
“Your men have desecrated God’s altars, slaughtered his servants, defiled his image, and stolen his tribute!” The king was angry now. One of his hands was clenched on the arm of his chair that was set in front of the altar, while the other hand was a fist that beat time with his accusations.
“Your god cannot look after himself?” Ubba enquired.
“Our god is a mighty god,” Edmund declared, “the creator of the world, yet he also allows evil to exist to test us.”
“Amen,” one of the priests murmured as Ivar’s interpreter translated the words.
“He brought you,” the king spat, “pagans from the north! Jeremiah foretold this!”
“Jeremiah?” Ivar asked, quite lost now.
One of the monks had a book, the first I had seen in many years, and he unwrapped its leather cover, paged through the stiff leaves, and gave it to the king who reached into a pocket and took out a small ivory pointer that he used to indicate the words he wanted.“Quia malum ego,” he thundered, the pale pointer moving along the lines,“adduco ab aquilone et contritionem magnam!”
He stopped there, glaring at Ivar, and some of the Danes, impressed by the forcefulness of the king’s words, even though none of them understood a single one of them, touched their hammer charms. The priests around Edmund looked reproachfully at us. A sparrow flew in through a high window and perched for a moment on an arm of the high wooden cross that stood on the altar. Ivar’s dread face showed no reaction to Jeremiah’s words and it finally dawned on the East Anglian interpreter, who was one of the priests, that the king’s impassioned reading had meant nothing to any of us.
“For I will bring evil from the north,” he translated, “and great destruction.”
“It is in the book!” Edmund said fiercely, giving the volume back to the monk.
“You can keep your church,” Ivar said carelessly.
“It is not enough!” Edmund said. He stood up to give his next words more force. “I will rule here,” he went on, “and I will suffer your presence if I must, and I will provide you with horses, food, coin, and hostages, but only if you, and all of your men, submit to God. You must be baptized!”
That word was lost on the Danish interpreter, and on the king’s, and finally Ubba looked to me for help.
“You have to stand in a barrel of water,” I said, remembering how Beocca had baptized me after my brother’s death, “and they pour more water over you.”
“They want to wash me?” Ubba asked, astonished.
I shrugged. “That’s what they do, lord.”
“You will become Christians!” Edmund said, then shot me an irritated look. “We can baptize in the river, boy. Barrels are not necessary.”
“They want to wash you in the river,” I explained to Ivar and Ubba, and the Danes laughed. Ivar thought about it. Standing in a river for a few minutes was not such a bad thing, especially if it meant he could hurry back to quell whatever trouble afflicted Northumbria. “I can go on worshipping Odin once I’m washed?” he asked.
“Of course not!” Edmund said angrily. “There is only one God!”
“There are many gods,” Ivar snapped back, “many! Everyone knows that.”
“There is only one God, and you must serve him.”
“But we’re winning,” Ivar explained patiently, almost as if he talked to a child, “which means our gods are beating your one god.”
The king shuddered at this awful heresy.
“Your gods are false gods,” he said. “They are turds of the devil, they are evil things who will bring darkness to the world, while our god is great, he is all powerful, he is magnificent.”
“Show me,” Ivar said.
Those two words brought silence. The king, his priests, and his monks all stared at Ivar in evident puzzlement.
“Prove it,” Ivar said, and his Danes murmured their support of the idea. King Edmund blinked, evidently lost for inspiration, then had a sudden idea and pointed at the leather panel on which was painted Saint Sebastian’s experience of being an archer’s target. “Our god spared the blessed Saint Sebastian from death by arrows,” Edmund said, “which is proof enough, is it not?”
“But the man still died,” Ivar pointed out.
“Only because that was God’s will.”
Ivar thought about that. “So would your god protect you from my arrows?” He asked.
“If it is his will, yes.”
“So let’s try,” Ivar proposed. “We shall shoot arrows at you, and if you survive then we’ll all be washed.”
Edmund stared at the Dane, wondering if he was serious, then looked nervous when he saw that Ivar was not joking. The king opened his mouth, found he had nothing to say, and closed it again, then one of his tonsured monks murmured to him and he must have been trying to persuade the king that God was suggesting this ordeal in order to extend his church, and that a miracle would result, and the Danes would become Christians and we would all be friends and end up singing together on the high platform in heaven. The king did not look entirely convinced by this argument, if that was indeed what the monk was proposing, but the Danes wanted to attempt the miracle now and it was no longer up to Edmund to accept or refuse the trial.
A dozen men shoved the monks and priests aside while more went outside to find bows and arrows. The king, trapped in his defense of God, was kneeling at the altar, praying as hard as any man has ever prayed. The Danes were grinning. I was enjoying it. I think I rather hoped to see a miracle, not because I was a Christian, but because I just wanted to see a miracle. Beocca had often told me about miracles, stressing that they were the real proof of Christianity’s truths, but I had never seen one. No one had ever walked on the water at Bebbanburg and no lepers were healed there and no angels had filled our night skies with blazing glory, but now, perhaps, I would see the power of God that Beocca had forever preached to me. Brida just wanted to see Edmund dead.
“Are you ready?” Ivar demanded of the king.
Edmund looked at his priests and monks and I wondered if he was about to suggest that one of them should replace him in this test of God’s power. Then he frowned and looked back to Ivar. “I will accept your proposal,” he said.
“That we shoot arrows at you?”
“That I remain king here.”
“But you want to wash me first.”
“We can dispense with that,” Edmund said.
“No,” Ivar said. “You have claimed your god is all powerful, that he is the only god, so I want it proved. If you are right then all of us will be washed. Are we agreed?” This question was asked of the Danes, who roared their approval.
“Not me,” Ravn said, “I won’t be washed.”
“We will all be washed!” Ivar snarled, and I realized he truly was interested in the outcome of the test, more interested, indeed, than he was in making a quick and convenient peace with Edmund. All men need the support of their god and Ivar was trying to discover whether he had, all these years, been worshipping at the wrong shrine. “Are you wearing armor?” he asked Edmund.
“No.”
“Best to be sure,” Ubba intervened and glanced at the fatal painting. “Strip him,” he ordered. The king and the churchmen protested, but the Danes would not be denied and King Edmund was stripped stark naked. Brida enjoyed that. “He’s puny,” she said. Edmund, the butt of laughter now, did his best to look dignified. The priests and monks were on their knees, praying, while six archers took their stance a dozen paces from Edmund.
“We are going to find out,” Ivar told us, stilling the laughter, “whether the English god is as powerful as our Danish gods. If he is, and if the king lives, then we shall become Christians, all of us!”
“Not me,” Ravn said again, but quietly so that Ivar could not hear. “Tell me what happens, Uhtred.”
It was soon told. Six arrows hit, the king screamed, blood spattered the altar, he fell down, he twitched like a gaffed salmon, and six more arrows thumped home. Edmund twitched some more, and the archers kept on shooting, though their aim was bad because they were half helpless with laughter, and they went on shooting until the king was as full of feathered shafts as a hedgehog has spikes. And he was quite dead by then. He was bloodied, his white skin redlaced, openmouthed, and dead. His god had failed him miserably.
Nowadays, of course, that story is never told; instead children learn how brave Saint Edmund stood up to the Danes, demanded their conversion, and was murdered. So now he is a martyr and a saint, warbling happily in heaven, but the truth is that he was a fool and talked himself into martyrdom.
The priests and monks wailed, so Ivar ordered them killed as well; then he decreed that Earl Godrim, one of his chiefs, would rule in East Anglia and that Halfdan would savage the country to quench the last sparks of resistance. Godrim and Halfdan would be given a third of the army to keep East Anglia quiet, while the rest of us would return to subdue the unrest in Northumbria. So now East Anglia was gone.
And Wessex was the last kingdom of England.








.jpg)